Choose Your Login Account
Thomson currently has two account systems - one for the website and CAD model downloads, and one for e-commerce. We understand that two logins is an inconvenience and are working to consolidate our systems into one login process. Until we’re able to consolidate the two logins, please follow these guidelines:
- Download CAD models
- Save and retrieve projects in LinearMotioneering® and MicronMotioneering® tools
- Access Distributor Extranet and all related resources
- Order directly from Thomson online (North America only)
- Authorized Thomson Distributors can view and order from quotes online (Global)
- View the shopping cart and look up prior direct orders
Przegląd
Why Choose Ball Screw Assemblies?
Ball screw assemblies provide an excellent method for translating rotational motion to linear motion for many applications, including those where high loads and close tolerances are required. To apply the correct type of ball screw and nut assembly in a particular application, the design engineer must consider the advantages and capabilities of each. Selecting the right technology can reduce design complexity, improve performance and reduce the overall cost of the assembly.
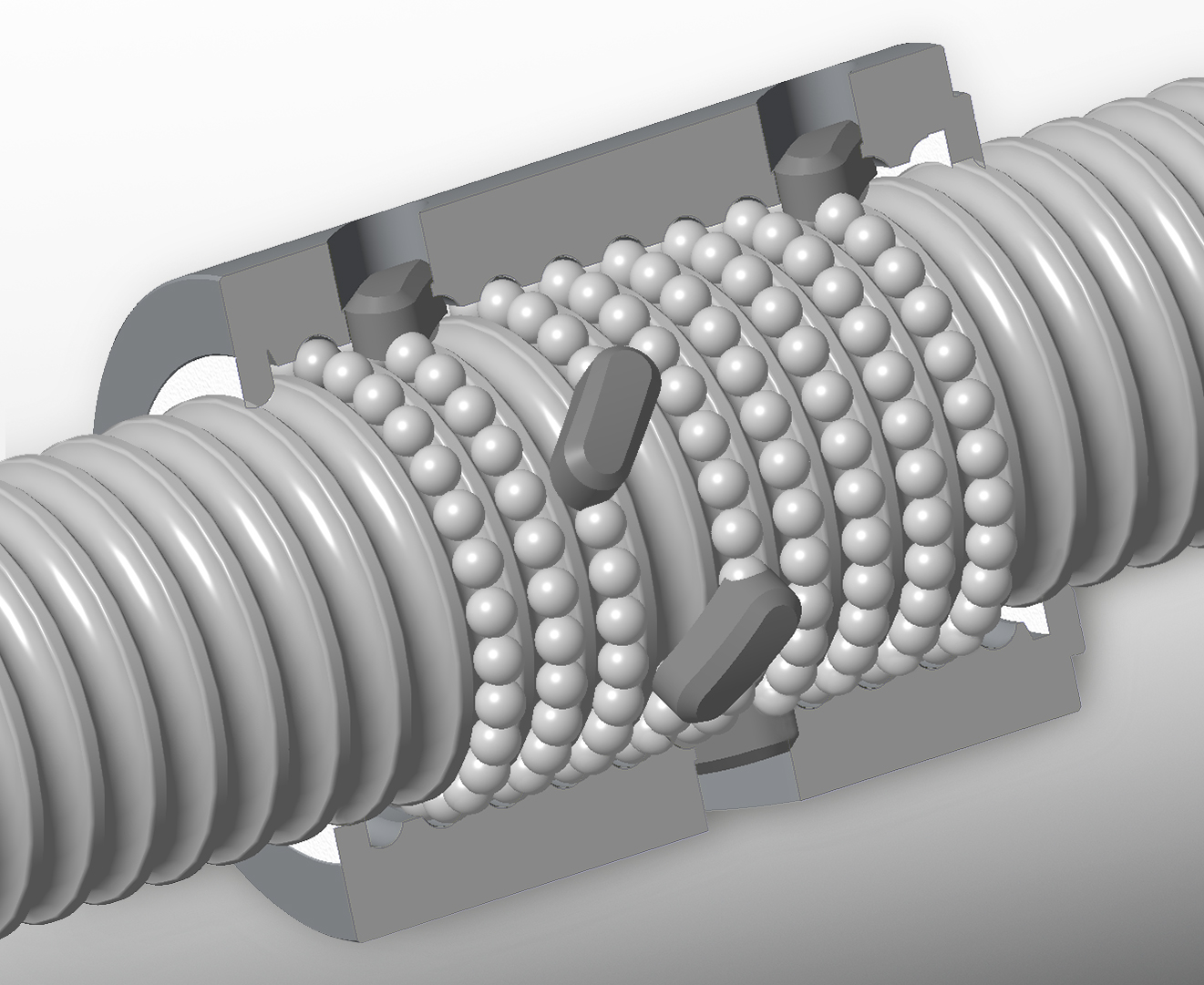
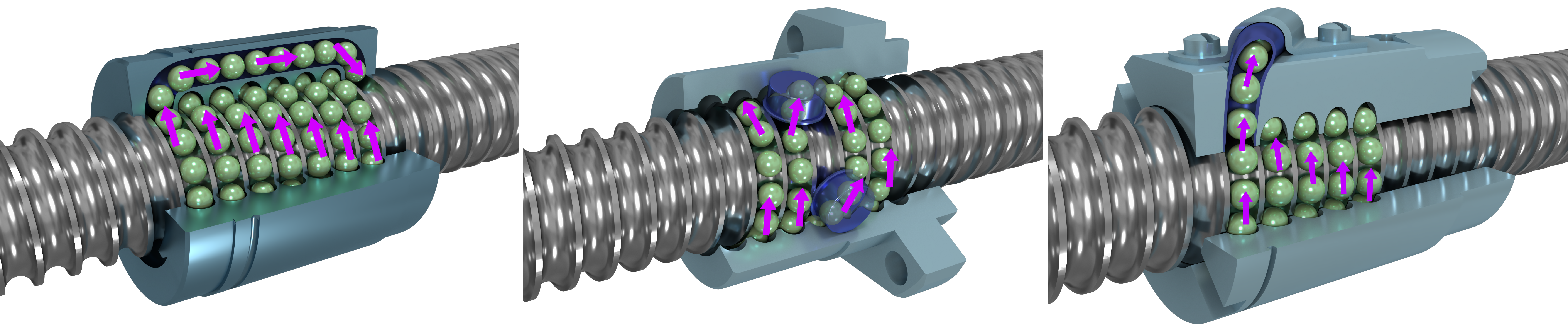
This image compares the three types of ball return systems (from left to right): internal, button and external.
Mounting Options
Ball screws are mounted in either supported or fixed configurations. A supported end holds the ball screw at one focal point and does not resist bending moments. A supported end is generally easier to align and install than a fixed one, so installation costs are typically lower. A fixed end resists bending moment loads because it is typically based on two bearings spaced sufficiently so the ball screw remains perpendicular to the planes of the rotary bearings. The fixed offers greater column strength and higher critical speed. The image below illustrates four fixity options.
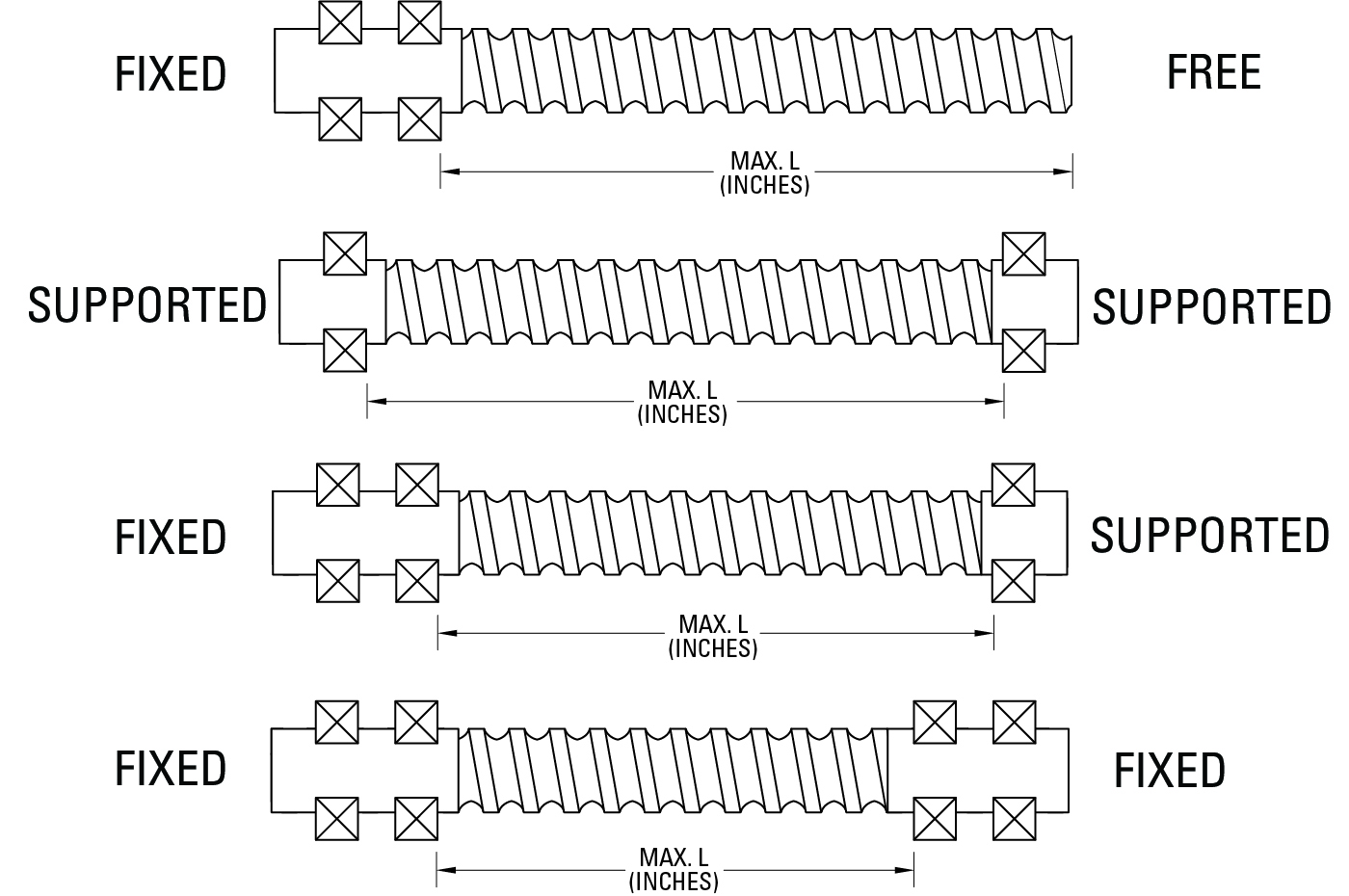
The assembly can be fixed at both ends, fixed at only one end and supported on the other, supported at both ends, or fixed at one end and free at the other.
Ball screw assemblies are not all alike. Whether it be metric ball screws, inch ball screws or miniature ball screws, key differences affect their performance and extend their lives. These include:
- Design. Through extensive research and evaluations, Thomson engineers have been able to develop a comprehensive ball screw offering that delivers optimal solutions for countless applications. Available in a full range of diameters, leads and ball nut configurations, in either pre-loaded or non-pre-loaded types, and all in industry standard envelopes, our ball screws provide dependable accuracy and repeatability at an economical price.
- Quality. With a vast background in countless applications, Thomson is uniquely positioned to provide the highest levels of quality across our full line of ball screw assemblies. Our fully equipped engineering laboratory performs qualification testing for mechanical performance, environmental effects and structural integrity. Your rotating ball screw nut assembly is inspected every step of the way to ensure top quality and performance.
- Materials. The materials used to manufacture ball screw assemblies are critical to their performance. Our in-house metallurgists control and verify that the materials used are of the highest quality. They can also select and recommend materials best suited to your particular application.
- Manufacturing. Thomson maintains the most modern and complete ball screw manufacturing facilities in the industry. In-house manufacturing capabilities include our proprietary heat treating and plating processes. Expert manufacturing using the most modern equipment available provides ball screw assemblies that set the standards for performance, precision and travel life.
- Application Support. Working with Thomson is like having your own staff of ball screw design engineers able to address application concerns and recommend solutions. Thomson field sales and applications engineering personnel have more ball screw expertise than any other group in the industry. They are skilled at evaluating your requirements and designing assemblies that fit your needs.
Jak mogę wykorzystać kulowe śruby pociągowe firmy Thomson?

FILM: Inteligentne siłowniki Thomson: projektowanie inteligentnych maszyn za pomocą inteligentnych narzędzi

VIDEO: Maximize Load Capacity, Lifecycle and Compactness of Your Linear Motion Designs
Any new application requires careful analysis of product performance, life and cost. Especially those that take on larger loads. Learn why you should be considering a high-load ball screw over standard ball screws for your next linear motion application.
Presenter: Markus Brändle, Product Line Specialist – Screws, Screw Jacks and LB&G Thomson Neff Industries, Germany

FILM: Wskazówki techniczne: jak załadować łożyska kulkowe do nakrętki kulowej serii metrycznej
Jak ponownie włożyć łożyska do nakrętki kulowej z powrotem przy użyciu przycisku? Często metryczne nakrętki kulowe są nakrętkami kulowymi z powrotem przy użyciu przycisku. Technika ta może być również stosowana do nakrętek z powrotem rurkowym.

FILM: Rozważania i obliczenia dotyczące wyboru właściwej kulowej śruby pociągowej do danego zastosowania
W jaki sposób spośród tysięcy możliwych opcji można szybko i pewnie zwymiarować i wybrać optymalne rozwiązanie kulowej śruby pociągowej do danego zastosowania ruchu liniowego?

FILM: Wskazówki techniczne: jak przenieść nakrętkę kulową na kulową śrubę pociągową
Jak zamontować nakrętkę kulową na śrubie od strony trzpienia.

Artykuły techniczne
-
Calowe czy metryczne kulowe śruby pociągowe: czy zadajesz właściwe pytania?
Ponieważ kulowe śruby pociągowe są dostępne zarówno w wymiarach calowych, jak i metrycznych, projektanci czasami rozpoczynają proces specyfikacji od wyboru rodziny produktów na podstawie jednostki miary. Taka decyzja może przedwcześnie wykluczyć idealny produkt do danego zastosowania i doprowadzić do znacznych strat czasu, pracy i kosztów. W tym artykule wyjaśniono, w jaki sposób pytania dotyczące wymiarowania i doboru skoncentrowane na wydajności — a nie na nazwach produktów — mogą prowadzić do bardziej efektywnych projektów ruchu liniowego.
Daha fazla bilgi -
Kulowe śruby pociągowe do dużych obciążeń — rozwiązanie do sterowania ruchem o większej gęstości obciążenia
Śruby rolkowe były propagowane jako jedyna technologia, którą można wybrać do przenoszenia dużych obciążeń, gdy rozmiar jest ograniczeniem.W rzeczywistości jednak postęp technologii kulowych śrub pociągowych umożliwia wykorzystanie ich również do zastosowań wymagających dużych obciążeń. Jest to istotne, ponieważ kulowa śruba pociągowa o wysokiej obciążalności jest zazwyczaj o połowę tańsza od porównywalnej śruby rolkowej o takich samych parametrach.
Daha fazla bilgi -
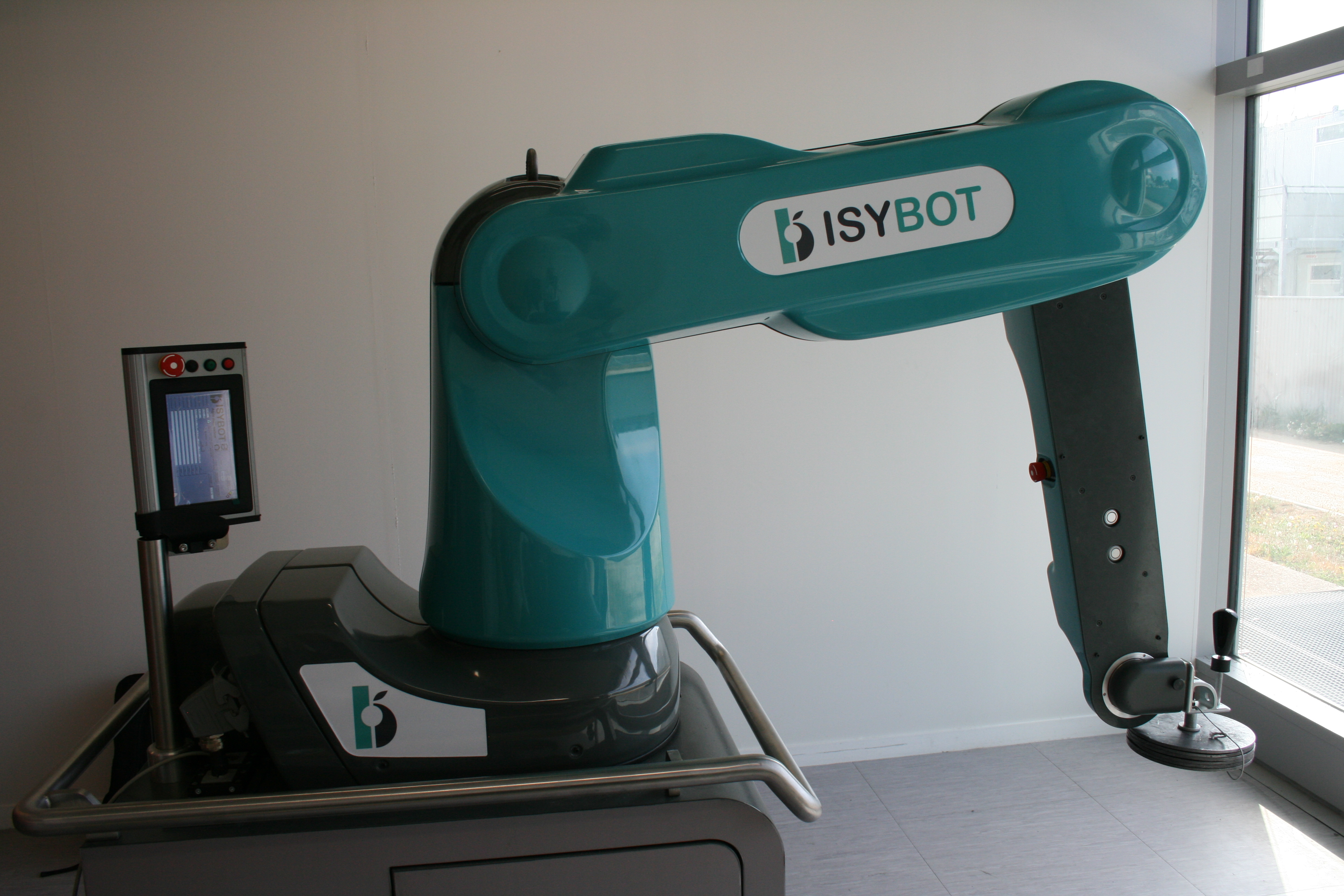
Kulowe śruby pociągowe — rozwiązanie w zakresie bezpiecznego i wydajnego ruchu kobotów
Roboty współpracujące (koboty), wykorzystywane na dużą skalę w zastosowaniach produkcyjnych, w których występują ciągłe operacje podnoszenia, ale nadal wymagany jest udział człowieka, zyskują coraz większą popularność. Francuski producent kobotów opracował rozwiązanie, które wykorzystuje kulowe śruby pociągowe i siłowniki linkowe zamiast przekładni, wyznaczając nowy standard wydajności i bezpieczeństwa kobotów.
Daha fazla bilgi
Broszury
Katalogi
Instrukcje obsługi
Technical Articles
| Thomson High-Load Ball Scews Provide Maximum Load Capacity and Longer Life in a Compact Envelope | 2019-02-04 |
Certifications
| ZESPOŁY ŚRUB KULOWYCH | |||
| Zespoły śrub kulowych – calowe |  |
— | — |
| Zespoły śrub kulowych – metryczne (Ameryka Północna) |  |
— | — |
| Zespoły śrub kulowych – metryczne (Europa) |  |
— | — |
| NAKRĘTKI KULOWE | |||
| Nakrętki kulowe kołnierzowe – calowe |  |
— | — |
| Nakrętki kulowe kołnierzowe – metryczne |  |
— | — |
| Nakrętki kulowe gwintowane – calowe |  |
— | — |
| Nakrętki kulowe gwintowane – metryczne |  |
— | — |
| Nakrętki kulowe cylindryczne – metryczne |  |
— | — |
| PODPORY KOŃCOWE | |||
| Podpory końcowe śrub kulowych – calowe |  |
— | — |
| Podpory końcowe śrub kulowych – metryczne |  |
— | — |
| ŚRUBY | |||
| Precyzyjne walcowane śruby kulowe – calowe |  |
— | — |
| Precyzyjne walcowane śruby kulowe – metryczne |  |
— | — |
| AKCESORIA | |||
| Kołnierze do śrub kulowych |  |
— | — |
| Pierścienie zgarniające do śrub kulowych |  |
— | — |
To provide better service to you on our websites, we and our service providers use cookies to collect your personal data when you browse. For information about our use of cookies and how to decline them or turn them off please read our cookie policy [available here].