Choose Your Login Account
Thomson currently has two account systems - one for the website and CAD model downloads, and one for e-commerce. We understand that two logins is an inconvenience and are working to consolidate our systems into one login process. Until we’re able to consolidate the two logins, please follow these guidelines:
- Download CAD models
- Save and retrieve projects in LinearMotioneering® and MicronMotioneering® tools
- Access Distributor Extranet and all related resources
- Order directly from Thomson online (North America only)
- Authorized Thomson Distributors can view and order from quotes online (Global)
- View the shopping cart and look up prior direct orders
Überblick
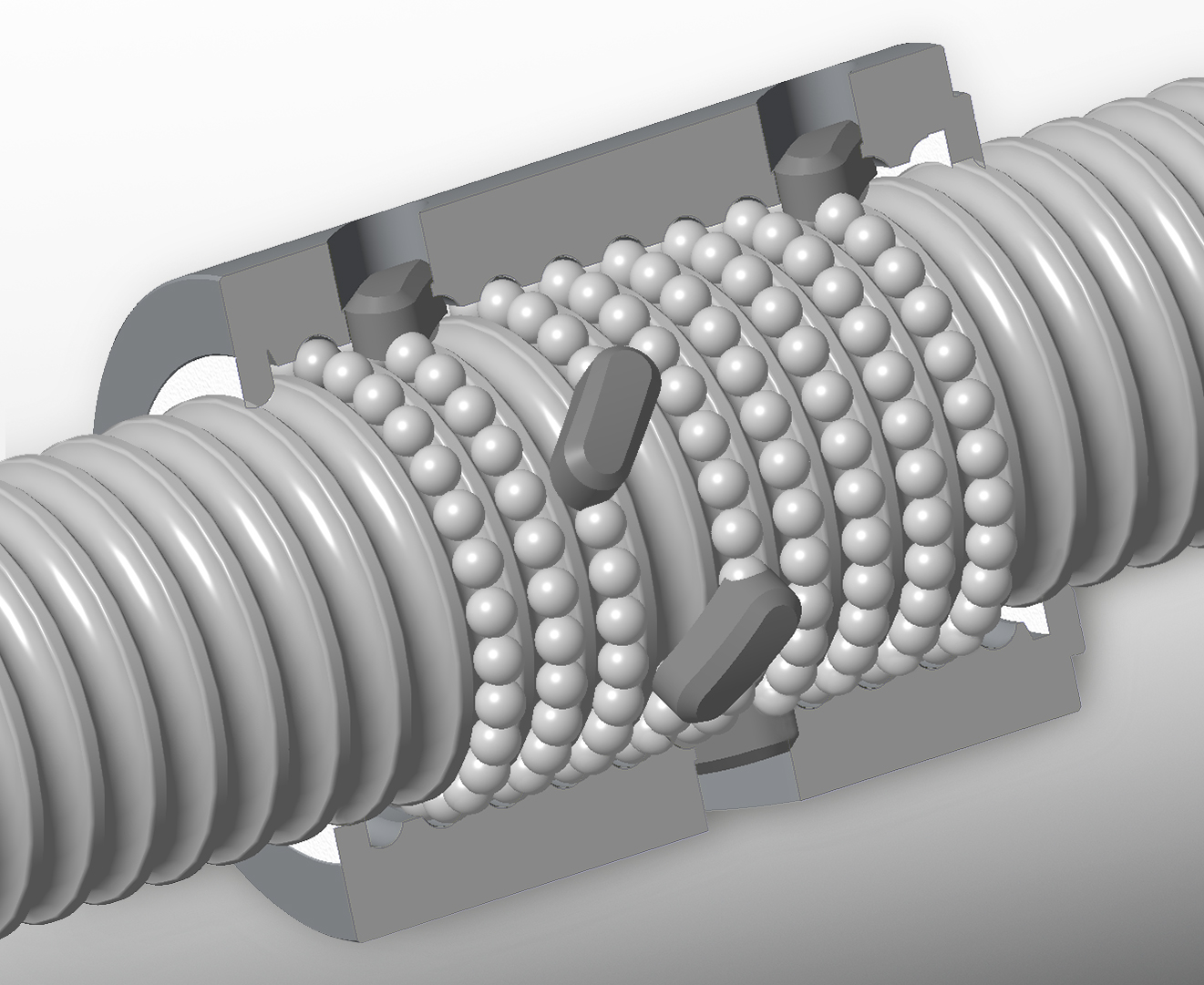
Why Choose Ball Screw Assemblies?
Ball screw assemblies provide an excellent method for translating rotational motion to linear motion for many applications, including those where high loads and close tolerances are required. To apply the correct type of ball screw and nut assembly in a particular application, the design engineer must consider the advantages and capabilities of each. Selecting the right technology can reduce design complexity, improve performance and reduce the overall cost of the assembly.
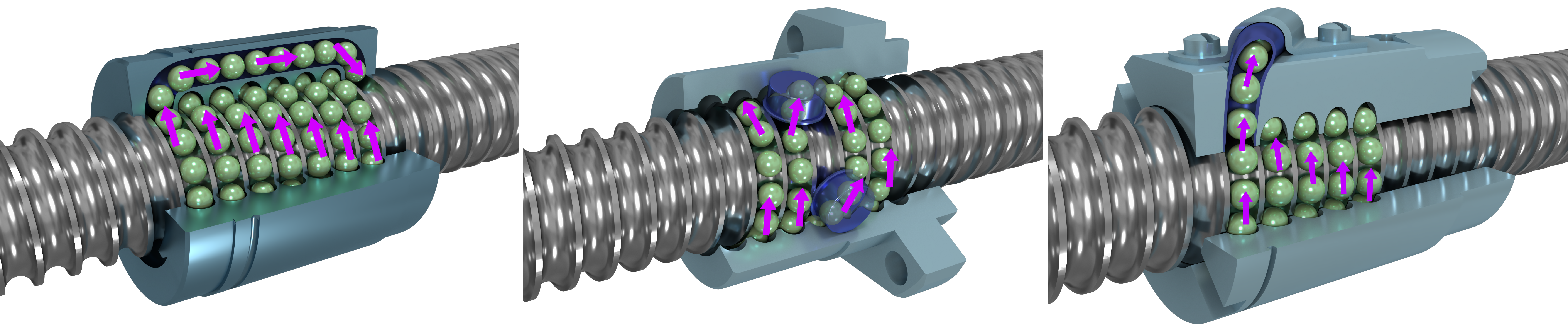
This image compares the three types of ball return systems (from left to right): internal, button and external.
Mounting Options
Ball screws are mounted in either supported or fixed configurations. A supported end holds the ball screw at one focal point and does not resist bending moments. A supported end is generally easier to align and install than a fixed one, so installation costs are typically lower. A fixed end resists bending moment loads because it is typically based on two bearings spaced sufficiently so the ball screw remains perpendicular to the planes of the rotary bearings. The fixed offers greater column strength and higher critical speed. The image below illustrates four fixity options.
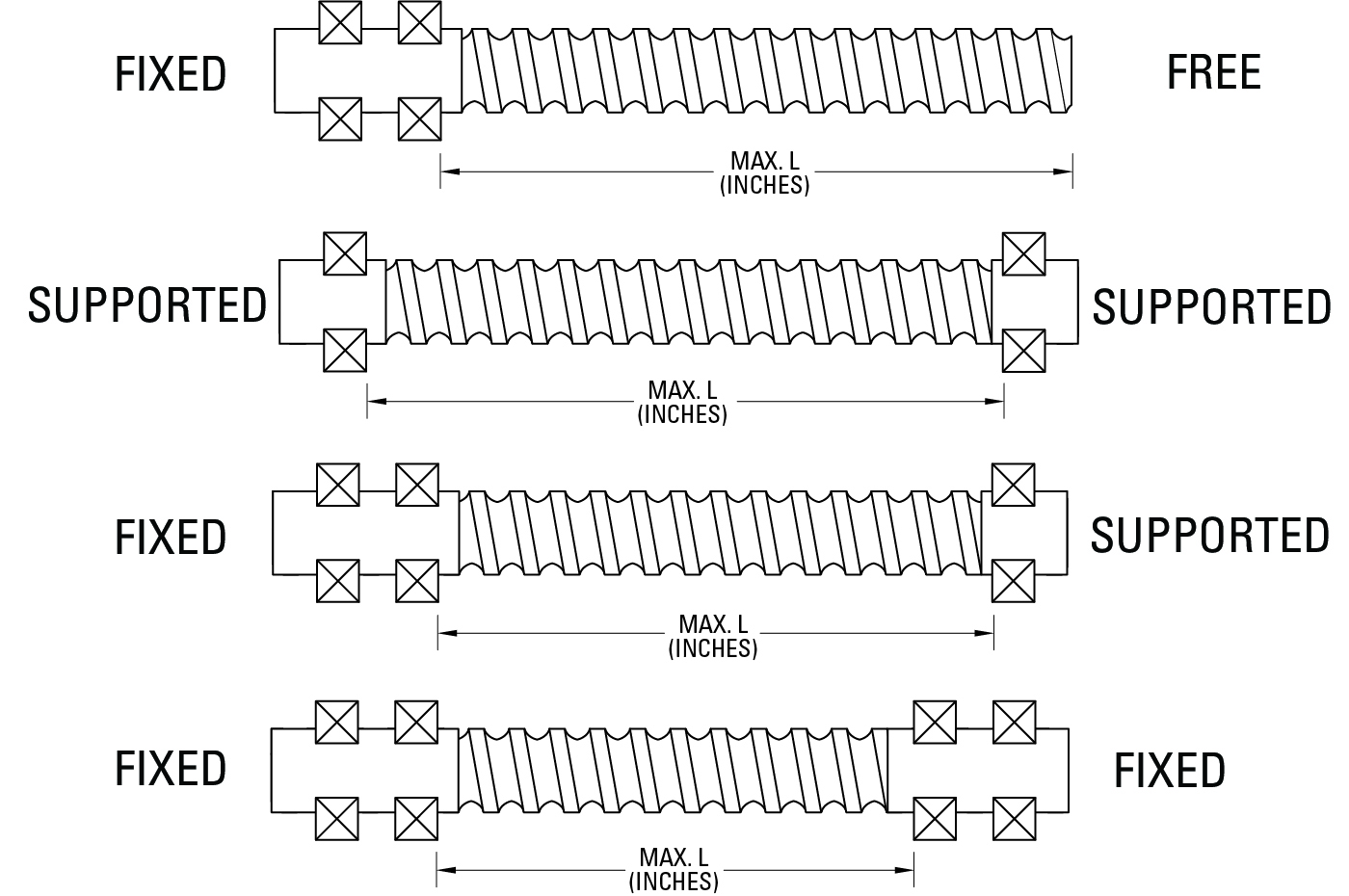
The assembly can be fixed at both ends, fixed at only one end and supported on the other, supported at both ends, or fixed at one end and free at the other.
Ball screw assemblies are not all alike. Whether it be metric ball screws, inch ball screws or miniature ball screws, key differences affect their performance and extend their lives. These include:
- Design. Through extensive research and evaluations, Thomson engineers have been able to develop a comprehensive ball screw offering that delivers optimal solutions for countless applications. Available in a full range of diameters, leads and ball nut configurations, in either pre-loaded or non-pre-loaded types, and all in industry standard envelopes, our ball screws provide dependable accuracy and repeatability at an economical price.
- Quality. With a vast background in countless applications, Thomson is uniquely positioned to provide the highest levels of quality across our full line of ball screw assemblies. Our fully equipped engineering laboratory performs qualification testing for mechanical performance, environmental effects and structural integrity. Your rotating ball screw nut assembly is inspected every step of the way to ensure top quality and performance.
- Materials. The materials used to manufacture ball screw assemblies are critical to their performance. Our in-house metallurgists control and verify that the materials used are of the highest quality. They can also select and recommend materials best suited to your particular application.
- Manufacturing. Thomson maintains the most modern and complete ball screw manufacturing facilities in the industry. In-house manufacturing capabilities include our proprietary heat treating and plating processes. Expert manufacturing using the most modern equipment available provides ball screw assemblies that set the standards for performance, precision and travel life.
- Application Support. Working with Thomson is like having your own staff of ball screw design engineers able to address application concerns and recommend solutions. Thomson field sales and applications engineering personnel have more ball screw expertise than any other group in the industry. They are skilled at evaluating your requirements and designing assemblies that fit your needs.
Wie Ihre Lineartechnik von Thomson Kugelgewindetrieben profitieren kann

VIDEO: Kugelgewindetriebe: Aufbau und Montage
Dieses Video behandelt den Aufbau und die Installation von Kugelgewindetrieben. Es erlätert die Funktion von Kugelgewindetrieben im Anwendungsdesign sowie die Komponenten eines Kugelgewindetriebes und einer Kugelgewindemutter. Außerdem wird die Montage einer Kugelgewindemutter auf eine Spindel dargestellt und das Einsetzen von Kugellagern für den Fall, dass einige Lager während der Montage herausfallen.

WEBINAR: Maximierung der Tragzahl, Lebensdauer und Kompaktheit Ihrer Linearsysteme
Jede einzelne Anwendung erfordert eine sorgfältige Analyse von Leistung, Lebensdauer und Kosten. Das gilt insbesondere bei hohen Lasten. Erfahren Sie, warum Sie bei Ihrer nächsten Nutzung eines Linearsystems einen Schwerlast- einem Standard-Kugelgewindetrieb vorziehen sollten.
Referent: Markus Brändle, Produktlinien-Verantwortlicher – Kugelgewindetriebe, Spindelhubgetriebe sowie Linearlager & -führungen bei Thomson Neff Industries, Deutschland

VIDEO: TechTips: Befüllen einer metrischen Kugelgewindemutter mit Lagerkugeln
Wiederbefüllen einer Kugelgewindemutter mit Lagerkugeln. Metrische Kugelgewindemuttern sind häufig mit einer Einzelumlenkung ausgestattet. Die gezeigte Methode eignet sich aber auch für Muttern mit Kanalumlenkung.

Webinaraufzeichnung: Überlegungen und Berechnungen zur Auswahl des geeigneten Kugelgewindetriebs für Ihre Anwendung
Wie wählen Sie aus all den Tausenden von Möglichkeiten schnell und zuverlässig für Ihre Linearanwendung den optimalen Kugelgewindetrieb in der passenden Größe?

VIDEO: TechTips: Aufbringen einer Kugelgewindemutter auf eine Spindel
So gelangt die Kugelgewindemutter sicher von der Transporthülse auf die Spindel.

Technische Artikel
-
Kugelgewindetriebe, Zollmaß oder metrisch: Stellen Sie die richtigen Fragen?
Da Kugelgewindetriebe sowohl in Zoll als auch in metrischen Maßen erhältlich sind, beginnen Konstrukteure zuweilen ihre Spezifikation mit der Auswahl einer Produktreihe nach diesem Unterscheidungsmerkmal. Diese Entscheidung kann jedoch das perfekte Produkt für die jeweilige Anwendung von vornherein ausschließen und zu deutlichen Nachteilen bezüglich Zeit-, Arbeits- und Kostenaufwand führen. Dieser Artikel erläutert, wie Auslegungs- und Auswahlfragen, die auf die Leistung abzielen – anstatt auf Produktnamen – effizientere Linearlösungen ergeben.
Mehr erfahren -
Hochlast-Kugelgewindetriebe – Aktorik mit höherer Lastdichte
Rollengewindetriebe galten seit langem als einzige Technologie zur Bewegung großer Lasten, wenn die Baugröße begrenzt ist. Tatsächlich haben Fortschritte in der Technologie von Kugelgewindetrieben die Möglichkeit eröffnet, auch für Anwendungen mit hohen Lasten eingesetzt zu werden. Das ist besonders wichtig, da ein Hochlast-Kugelgewindetrieb in der Regel nur halb so teuer ist wie ein Rollengewindetrieb mit vergleichbaren Leistungswerten.
Mehr erfahren -
Kugelgewindetriebe – die Lösung für sichere und effiziente Antriebe in Cobots
In der Massenproduktion, wo repetitive Hubbewegungen ausgeführt werden, aber dennoch manuelle Eingriffe erforderlich sind, erlangen sogenannte „kollaborative Roboter“ (Cobots) immer mehr an Beliebtheit. Ein französischer Cobot-Hersteller hat nun eine Lösung entwickelt, die anstelle von Zahnrädern Aktuatoren mit Kugelgewindetrieb und Seilzug nutzt und damit einen neuen Maßstab in puncto Effizienz und Sicherheit für Cobots setzt.
Mehr erfahren
Broschüren
Kataloge
Handbücher
Technical Articles
| Thomson High-Load Ball Scews Provide Maximum Load Capacity and Longer Life in a Compact Envelope | 2019-02-04 |
Certifications
| KUGELGEWINDETRIEBE | |||
| Kugelgewindetriebe - Zoll |  |
— | — |
| Kugelgewindetriebe - metrisch (Nordamerika) |  |
— | — |
| Kugelgewindetriebe - metrisch (Europa) |  |
— | — |
| KUGELGEWINDEMUTTERN | |||
| Flansch-Kugelgewindemuttern – Zoll |  |
— | — |
| Flansch-Kugelgewindemuttern – metrisch |  |
— | — |
| Einschraub-Kugelgewindemuttern - Zoll |  |
— | — |
| Einschraub-Kugelgewindemuttern - metrisch |  |
— | — |
| Zylindrische Kugelgewindemuttern – metrisch |  |
— | — |
| WELLENBÖCKE | |||
| Kugelgewindetrieb-Wellenböcke - Zoll |  |
— | — |
| Kugelgewindetrieb-Wellenböcke - metrisch |  |
— | — |
| SPINDELN | |||
| Präzisionsgerollte Kugelgewindespindeln - Zoll |  |
— | — |
| Präzisionsgerollte Kugelgewindespindeln - metrisch |  |
— | — |
| ZUBEHÖR | |||
| Kugelgewindetriebe - Flansche |  |
— | — |
| Kugelgewindetriebe - Abstreifer |  |
— | — |
To provide better service to you on our websites, we and our service providers use cookies to collect your personal data when you browse. For information about our use of cookies and how to decline them or turn them off please read our cookie policy [available here].