Choose Your Login Account
Thomson currently has two account systems - one for the website and CAD model downloads, and one for e-commerce. We understand that two logins is an inconvenience and are working to consolidate our systems into one login process. Until we’re able to consolidate the two logins, please follow these guidelines:
- Download CAD models
- Save and retrieve projects in LinearMotioneering® and MicronMotioneering® tools
- Access Distributor Extranet and all related resources
- Order directly from Thomson online (North America only)
- Authorized Thomson Distributors can view and order from quotes online (Global)
- View the shopping cart and look up prior direct orders
Customer Service Chat (ONLINE) Customer Service Chat (OFFLINE)
Overview
MS (MicroStage) Specifications:
| Specifications / Shaft Size | MS25 | MS33 |
|---|---|---|
| Profile size (w x h): mm | 50 x 25 | 60 x 33 |
| Type of screw | lead screw | lead screw |
| Max Stroke Length: mm (in) | 705.5 (27.8) | 704 (27.7) |
| Max Linear Speed: m/s (in/s) | 0.85 (33.5) | 1.02 (40.2) |
| Max Acceleration: m/s2 (in/s2) | 9.8 (386) | 9.8 (386) |
| Repeatability: ± mm (in) | 0.005 (0.0002) | 0.005 (0.0002) |
| Accuracy: mm/300mm (in/12in) | 0.2 (0.008) | 0.2 (0.008) |
| Max Input Speed: rpm | 2000 | 2000 |
| Temperature Range: °C (°F) | -20 to 80 (-4 to 176) |
-20 to 80 (-4 to 176) |
| Max Dynamic Load Fx: N (lbf) | 17.8 (4.0) | 80.1 (18.0) |
| Max Dynamic Load Fy: N (lbf) | 100 (22.5) | 150 (33.7) |
| Max Dynamic Load Fz: N (lbf) | 100 (22.5) | 150 (33.7) |
| Max Dynamic Load Torque (Mx): Nm (lbf-in) |
1.4 (12.4) | 2.8 (24.8) |
| Max Dynamic Load Torque (My): Nm (lbf-in) |
1.3 (11.5) | 2.5 (22.4) |
| Max Dynamic Load Torque (Mz): Nm (lbf-in) |
2.7 (23.9) | 5.1 (45.1) |
| Max Drive Shaft Force: N (lbf) | 222 (49.9) | 222 (49.9) |
| Max Drive Shaft Torque: Nm (lbf-in) |
0.08 (0.71) | 0.43 (3.81) |
| Lead screw diameter: mm (in) | 6.35 (0.25) | 9.53 (0.38) |
| Lead screw lead: inch leads (in) metric leads (mm) |
0.025, 0.05, 0.062, 0.2 ,0.25 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.3 1.5, 2, 3 |
.0625, 0.1, .125, 0.2 .375, 0.5, 1.0, 1.2 2 |
| Weight: kg (lb) unit with zero stroke every 100 mm of stroke each carriage |
0.47 (1.04) 0.18 (0.40) 0.07 (0.15) |
0.69 (1.52) 0.31 (0.68) 0.12 (0.27) |
MS (MicroStage) Feature Highlights:
- Double LinearRace rail assembly
- Unique bearing segment design
- Integrated ball or lead screw
- Ultra compact
- Complete axis solution
- Rugged but light-weight
- Flexible mounting configuration
- Low friction
- Low drive torque
- No stick-slip
- High precision
- Aircraft-grade extruded aluminum base
- Stroke lengths to 900 mm
Brochures
| Linear Motion Systems | 1257 KB | |
| Linear Motion Systems | 1425 KB | |
| Miniature Components and Systems | 1527 KB | |
| Miniature Components and Systems | 1524 KB | |
| Miniature Components and Systems | 1626 KB |
Catalogs
| Linear Motion Systems | 9860 KB | |
| Linear Motion Systems | 8137 KB | |
| Linear Motion Systems | 7983 KB | |
| Linear Motion Systems | 16431 KB |
Calculation Support
Data Sheets
| MicroStage MS46 Screw Drive | 91 KB |
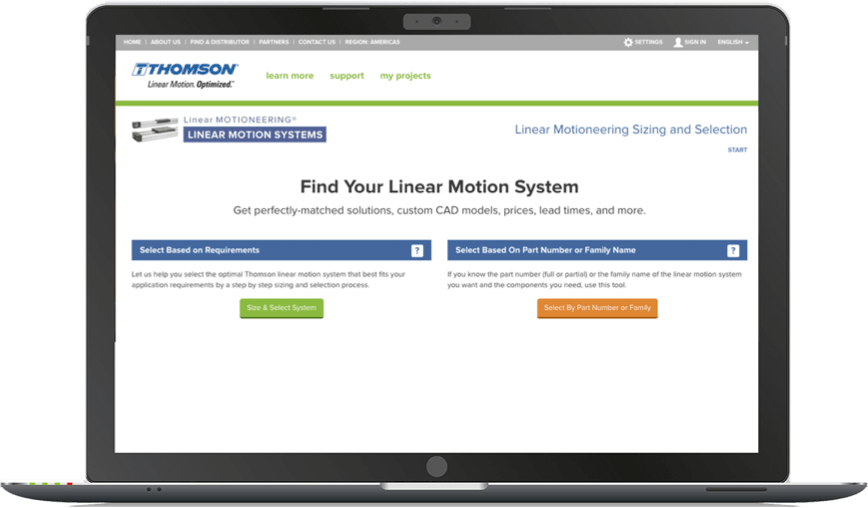
The Linear Motion Systems Product Selector is Temporarily Unavailable
Click the button below to use the newest edition of our industry's most advanced sizing and selection tool for linear motion system: LinearMotioneering.
Family
Drive Type
Guide Type
Repeatability
Nut Type
Stroke
Travel per Revolution
Carriage
Protection
Shaft Orientation
Shaft Quantity
Left Side (angle), First End (inline)
Right side (angle), Other end (inline)
Compare
3D Model
Family
Select system by product family.
Drive Type
- Ball Screw – A ball screw is installed down the length of the unit with the ball nut connected to the carriage. The input shaft is the end of the ball screw.
- Ball Screw, Left/Right – A ball screw with left hand threads on one end and Right hand threads on the other end is used. Rotating the input shaft will move the two carriages on the unit towards each other or away from each other.
- Lead Screw – Same as the ball screw drive but using a lead screw and nut
- Belt Drive – The input shaft is attached to a pulley which pulls a belt that is attached to the carriage.
- Non Drive – No drive system is installed in the unit. The assembly will support and guide the load but an external force will need to move it.
Ball Screw Drive
A ball screw is made up of a rotating screw and a moving ball nut. The ball nut is attached to the carriage of the unit. It does not have a normal thread, instead balls circulate inside the nut making it work as an efficient ball bearing that travels along the screw. Ball screws come in a large variety of leads, diameters and tolerance classes. The tolerance class (T3, T5, T7 or T9) indicates the lead tolerance of the screw. The lower the number, the higher the tolerance. High load capability and high accuracy are typical features of ball screw driven units.
Left/right Moving
Units with left/right moving have two carriages moving in opposite directions when the drive shaft is rotated. This type of unit has a ball screw where half of the screw has a left hand thread and the other half a right hand thread.
Belt Drive
A belt drive consists of a toothed belt which is attached to the carriage of the unit. The belt runs between two pulleys positioned at either end of the profile. One pulley is attached to the motor via the drive shaft in the drive station while the other is mounted in a tension station. The belts are made of plastic reinforced with steel cords. High speeds, long stroke, low noise and low overall weight are typical features of belt driven units.
Non Driven Linear Motion Systems
A non driven linear motion system has no drive shaft or any type of transmission. In reality a non driven linear motion system is a guide that has the same look and outer dimensions as the driven version. Normally a non driven unit is used together with a parallel working driven unit that are mechanically linked where the non driven unit help to share to load with the driven one.
Guide Type
- Ball – The carriage of the unit is supported on a recirculating ball guide system.
- Prisim – The carriage of the unit is supported on a guide system that is two surfaces sliding on each other.
- Wheel – The carriage of the unit is supported on a guide system that utilizes wheels in a track
- No guides – The system does not have a guide system that can guide external loads. It can only provide a thrust component.
Ball Guides
A ball guide consists of a ball rail and a ball bushing. The ball rail is made of hardened steel and runs along the inside of the profile. The ball bushing is attached to the carriage of the unit and contains balls that roll against the rail. The balls in the bushing can be recirculating or have fixed ball positions depending on the type of ball guide. The recirculating type has a longer life and better load capability while the fixed type typically is much smaller. Thomson uses three major types of ball guides in its linear motion systems. Either the compact single rail type with recirculating ball bushing (A), the stronger double rail type also with recirculating ball bushings (B) or the fixed ball position ball bushings type (not shown) which require very little space and are used in the smallest units. Ball guides offer high accuracy, high loads and medium speed.
Prisim or Slide Guides
A slide guide consist of a guide attached to the inside of the profile and a slide bushing attached to the carriage. The guide can be made of different materials (e.g. polished hardened steel, anodized aluminum) while the bushing is made of a polymer material. There are two types of bushings, fixed and prism. Prism bushings can move in relation to the guide which results in longer life and higher load capabilities. Slide bushings are silent, simple, reliable and robust and can be used in dirty and dusty environments. They are also resistant to shock loads, have a long life expectancy and require little or no maintenance.
Wheel Guides
A wheel guide consists of ball bearing wheels that run on a hardened steel rail. Wheel guides are a simple and robust guiding method offering high speeds, high loads and medium accuracy.
Non Guided Linear Motion Systems
A non guided linear motion system has a drive shaft and a ball screw but no guides. In reality a non guided linear motion system is a enclosed ball screw assembly with a carriage that has the same look and outer dimensions as the driven version. Using a non guided unit requires some kind of external guide to which the carriage can be attached.
Repeatability
Repeatability is the ability for a positioning system to return to a location. Some of the factors that affect the repatability are the angular repeatability of the motor, drive and motion control system, system friction and changes in load, speed and deceleration.
Nut Type
In ball screw driven units there are several nut styles used.
- Non Preloaded – The nut has back lash.
- Double nut preload – The system uses two ball nuts to obtain a zero lash preloaded assembly.
- Preloaded – The system uses a single preloaded nut that has zero lash.
Double Ball Nuts
Using double ball nuts will increase the repeatability of the unit. The ball nuts are installed so that they are pre-tensioned against each other eliminating the play between the nuts and the screw. A double nut unit will have a slightly shorter stroke for a given overall length.
Stroke
The stroke is the length that the carriage can travel from one end of the unit to the other. However, using the maximum stroke means that the carriage will collide with the ends of the profile due to braking and deceleration. The practical usable stroke is therefore shorter. We recommend that you specify a unit that have at least 100 mm longer stroke than the maximum stroke you need so that the unit can stop before colliding with the ends and also allow for some adjustment of the unit postition at the mounting.
Travel per Revolution
How far the carriage will advance with one turn of the input shaft.
Carriage
- Double Standard Carriages – Two standard length carriages. One driven one non driven.
- Double Short Carriages – Two shorter length carriages. One driven one non driven.
- Single Standard Carriage – One Standard length carriage
- Single Long Carriage – One Longer length carriage
- Single Short Carriage – One shorter length carriage
- Each Direction, Standard Carriage – Two standard length carriages. Each carriage with their only ball nut driven towards or away from each other.
- Each Direction, Short Carriage – Two short length carriages. Each carriage with their only ball nut driven towards or away from each other.
Protection
All units are designed for use in normal industrial environments. Units which have an open profile (i.e. have no cover band) are more sensitive to dust, dirt and fluids. These units require some kind of cover if they are used in environments where dust, dirt or fluids are present. Wash down or enhanced wash down protection can be ordered for our closed profile units. In all cases where a unit will be exposed to aggressive chemicals, heavy vibrations or other potentially harmful processes we recommend that you contact us for further advice.
Shaft Orientation
- Inline – The input shaft is in line with the axis of travel of the unit. These units use a screw drive.
- Right Angle – The input shaft is at 90 degrees to the axis of travel. These units use a belt drive.
Drive Shaft Orientation:
The drive shaft is the is the shaft to which the motor is connected, either directly, via a bell house flange or via a gear box. There are many sizes and types of drive shafts, such as shafts with or without key way or hollow shafts, depending on the type and size of the unit. Belt driven units can often have two drive shafts (same or different type and size), one on each side of the drive station, while screw driven only have on pointing out of the end of the unit. Customized drive shafts are possible, please contact customer service for more information.
Shaft Quantity
- Double shafts - there are two shafts on the units. One on each side for belt driven (right angle) units. One on each end for screw driven units.
- Single shaft – there is only one input shaft on the unit.
Left Side (angle), First End (inline)
The type of shaft on the Left side of a belt driven (right angle) unit or on one end of the inline (screw driven) units.


Right side (angle), Other end (inline)
The type of shaft on the Right side of a belt driven (right angle) unit or on the other end of double shaft inline (screw driven) units.


Customer Service
This part number is not available for sale online but may still be available for sale. Click here to contact Thomson Customer Support.
Customer ServiceTo download the models below, you will need to sign in.
To provide better service to you on our websites, we and our service providers use cookies to collect your personal data when you browse. For information about our use of cookies and how to decline them or turn them off please read our cookie policy [available here].

